

Customer relationship management
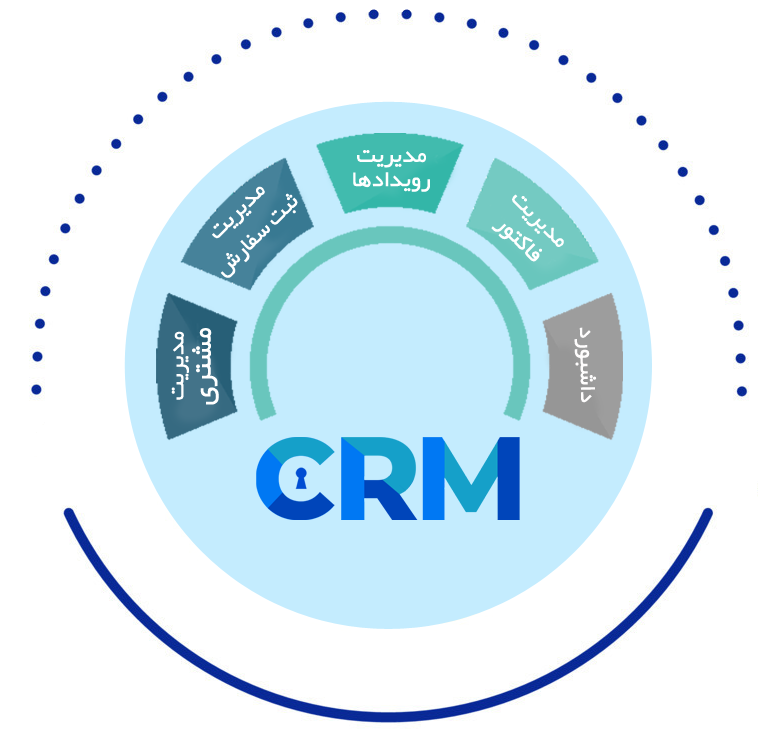
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a system for managing a company’s interactions with current and future customers. It often involves using technology to organize, automate and synchronize sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support.
CRM Solutions
CRM Solutions come with many features and tools and it's important for a company to choose a product based on their specific organizational needs. Most vendors will present information on their respective websites:
- Features These are what the product actually does and what value it can provide to an organization.
- Support Many CRM vendors have a basic level of support which generally only includes email and/or access to a support forum. Telephone support is often charged in either an annual or ad hoc pricing strategy. Some companies offer on-site support for an extra premium.
- Pricing This will be shown either per-user or as a flat price for a number of users. Vendors charge annually, quarterly, or monthly with variable pricing options for different features.
- Demonstration Periods Many vendors offer a trial period and/or online demonstrations.
Characteristics of CRM
- Relationship management is a customer-oriented feature with service response based on customer input, one-to-one solutions to customers’ requirements, direct online communications with customer and customer service centers that help customers solve their issues.
- Sales force automation. This function can implement sales promotion analysis, automate tracking of a client’s account history for repeated sales or future sales, and also сoordinate sales, marketing, call centers, and retail outlets in order to realize the salesforce automation.
- Use of technology. This feature is about following the technology trend and skills of value delivering using technology to make “up-to-the-second” customer data available. It applies data warehouse technology in order to aggregate transaction information, to merge the information with CRM solutions, and to provide KPI (key performance indicators).
- Opportunity management. This feature helps the company to manage unpredictable growth and demand and implement a good forecasting model to integrate sales history with sales projections.
- CRM in developing and maintaining client relationships
Marketing and Customer Service
Customer relationship management systems track and measure marketing campaigns over multiple networks. These systems can track customer analysis by customer clicks and sales. Places where CRM is used include call centers, social media, direct mail, data storage files, banks, and customer data queries.
CRM in customer contact centers
CRM systems are customer relationship management platforms. The goal of the system is to track, record, store in databases, and then determine the information in a way that increases customer relations (predominantly increased ARPU, and decreased churn). The CRM codifies the interactions between you and your customers so that you can maximize sales and profit using analytics and KPIs to give the users as much information on where to focus their marketing and customer service to maximize revenue and decrease idle and unproductive contact with your customers. The contact channels (now aiming to be omni-channel from multi-channel) use such operational methods as contact centers. The CRM software is installed in the contact centers, and help direct customers to the right agent or self-empowered knowledge. CRM software can also be used to identify and reward loyal customers over a period of time.
Growing in popularity is the idea of gamifying customer service environments. The repetitive and tedious act of answering support calls all day can be draining, even for the most enthusiastic customer service representative. When agents are bored with their work, they become less engaged and less motivated to do their jobs well. They are also prone to making mistakes. Gamification tools can motivate agents by tapping into their visceral need for reward, status, achievement, and competition.
CRM in B2B (Business-to-Business) market
The modern environment requires one business to interact with another via the web. According to a Sweeney Group definition, CRM is “all the tools, technologies and procedures to manage, improve, or facilitate sales, support and related interactions with customers, prospects, and business partners throughout the enterprise”. It assumes that CRM is involved in every B2B transaction.
Despite the general notion that CRM systems were created for the customer-centric businesses, they can also be applied to B2B environments to streamline and improve customer management conditions. B2C and B2B CRM systems are not created equally and different CRM software applies to B2B and Business-to-Customer (B2C) conditions. B2B relationships usually have longer maturity times than B2C relationships. For the best level of CRM operation in a B2B environment, the software must be personalized and delivered at individual levels.
Implementing CRM to the company
The following are general guidelines on implementing a CRM system.
- Make a strategic decision on what problems you want your CRM system to address, what improvements or changes it should bring in the business processes of the organization.
- Choose an appropriate project manager. Typically IT will be engaged, however a manager with a customer service/sales and marketing business focus should be involved, as the impact of the project will be mainly on the business side.
- Ensure executive sponsorship and top management support.
- Empower team members with the required authority to complete the tasks.
- Select the correct implementation partner. They must have both vertical and horizontal business knowledge, as well as technical expertise.
- Define KPI's that will measure the project's success
- Use a phased approach. Work towards long-term enterprise-scale implementation through a series of smaller, phased implementations
Differences between CRM for B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Customers)
B2B and B2C marketing operates differently, that is why they cannot use the same software. All the differences are focused on the approach of these two types of businesses:
- B2B companies have smaller contact databases than B2C
- The amount of sales in B2B is relatively small
- In B2B there is less figure propositions, but in some cases they cost a lot more than B2C items
- Relationships in B2B environment are built over a longer time
- B2B CRM must be easily integrated with other companies’ IT-solutions. Such integration enables the creation of forecasts about customer behavior based on their buying history, bills, business success, etc.
- An application for a B2B company must have a function to connect all the contacts, processes and deals among the customers segment and then prepare a paper
- Automation of sales process is an important requirement for B2B solutions. It should effectively manage the deal and progress it through all the phases towards signing
- A crucial point is personalization. It helps the B2B company to save strong and long-lasting relationships with the customer. To communicate with them more effectively, there should be integration with the email solutions
SaaS CRM Software
Often referred to as "on-demand" software, SaaS based software is delivered via the Internet and does not require installation on your computer. Instead, you'll generally access the software via your web browser. Businesses using the software do not purchase the software, and typically pay a subscription fee to the software vendor.
Small business
For small businesses a CRM system may simply consist of a contact manager system which integrates emails, documents, jobs, faxes, and scheduling for individual accounts.[citation needed] CRM systems available for specific markets (legal, finance) frequently focus on event management and relationship tracking as opposed to financial return on investment (ROI).
Social media
CRM often makes use of social media to build up customer relationships. Some CRM systems integrate social media sites like Twitter, LinkedIn and Facebook to track and communicate with customers sharing their opinions and experiences with a company, products and services. Enterprise Feedback Management software platforms such as Confirmit, Medallia, and Satmetrix combine internal survey data with trends identified through social media to allow businesses to make more accurate decisions on which products to supply.
Non-profit and membership-based
Systems for non-profit and also membership-based organizations help track constituents, fund-raising, Sponsors demographics, membership levels, membership directories, volunteering and communication with individuals.
Customer-centric relationship management (CCRM)
CCRM is a style of customer relationship management that focuses on customer preferences instead of customer leverage. This is a nascent sub-discipline of traditional customer relationship management; to take advantage of changes in communications technology.
Customer centric organizations help customers make better decisions and it also helps drive profitability. CCRM adds value by engaging customers in individual, interactive relationships.
Customer-centricity differs from client-centricity in that the latter refers almost exclusively to business-to-business models rather than customer-facing firms.
Features of CCRM
Customer-centric relationship management is used in marketing, customer service and sales, including:
- tailored marketing
- one-to-one customer service
- retaining customers
- building brand loyalty
- providing information customers actually want
- Subscription billing
- Rewards
Reference: www.wikipedia.org







یک نظر اضافه کنید
شماره موبایل شما منتشر نخواهد شد.زمینه های مورد نیاز هستند علامت گذاری شده *
امتیاز شما